Deallab analyzes the aero engine industry’s global market share, revenue ranking, and market size. The report also provides an overview and trends of the world’s leading aero engine manufacturers, including GE, Rolls-Royce, and Pratt & Whitney, the three aero engine giants, followed by Honeywell and Safran.
Global Market Share
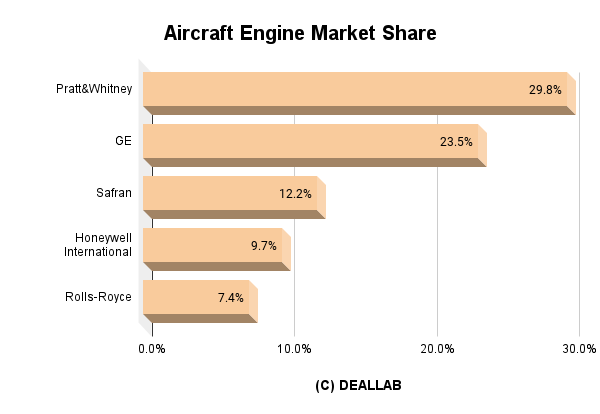
Using the aircraft engine manufacturers’ sales in 2021 as the numerator and the market size of the industry as the denominator, Deallab can simply estimate the global market share of the aircraft engine industry in 2021: Pratt & Whitney (Raytheon) in 1st place, GE in 2nd place, Safran in 3rd place.
Global Share of Aircraft Engines in 2021
| Ranking | Company | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pratt&Whitney | 29.8% |
| 2 | GE | 23.5% |
| 3 | Safran | 12.2% |
| 4 | Honeywell International | 9.7% |
| 5 | Rolls-Royce | 7.4% |
In the field of turbojet aircraft engines, Pratt & Whitney, a Raytheon company, is ranked first in the world. GE is the world’s second largest manufacturer of wide-body aircraft engines, and GE also has strength in wide-body aircraft engines. CFM International, a joint venture between GE and Snecma, a subsidiary of Safran of France, is responsible for engines for narrow-body aircraft. In 2014, GE sold its gas turbine and compressor business for the electric power industry to Germany’s Siemens, and is now concentrating on aircraft engines. In fifth place is Honeywell of the United States.
In the reciprocating engine segment, the market is split between Lycoming Engines, a Textron subsidiary, and Continental Motors of the United States, a subsidiary of China’s AVIC International. Narrow-body aircraft engines include MTU Aero Engines Germany and IAE International, a joint venture of the Japanese Alliance.
Market Size
Deallab calculates the market share of the aeroengine industry based on published data from research firms and other sources, assuming a global market size of $60.8 billion in 2021. The published statistical data referred to are as follows.
According to the research firm MarketsandMarkets, the market size of the industry in 2021 is US$60.8 billion; it is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.9% from 2021 to 2026, to US$92.9 billion by 2026. The lifting of travel restrictions will be the driver of growth in the short term, while increased demand for fuel-efficient aircraft engines will be the driver of growth in the medium to long term.
According to research firm Research and Markets, the global market for the industry is estimated to be worth $78 billion in 2020; it is expected to reach $82.2 billion in 2021 and grow at a CAGR of 5.64% to reach $108.5 billion by 2026.
According to research firm Fortune Business Insights, the industry’s market size is $79.9 billion in 2019; it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.3% through 2027. According to research firm T4, the industry was worth $73 billion in 2019 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 1% through 2025.
| Year | Market Size (USD bn) | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 60.8b | 8.9% |
| 2020 | 78 | 5.64% |
| 2019 | 73-82.2 | 1-11.3% |
Two or four aero engines are installed per aircraft. Demand for aircraft is expected to increase in the future, and the market for aircraft engines is also expected to grow. Aircraft engines also require continuous after-sales service, including periodic replacement, so repair parts and services are a source of revenue for aircraft engine companies as recurring income. On the other hand, because of the high durability and safety requirements, development and production will take a long time and place a heavy financial burden on the companies, and the oligopolistic market structure is expected to continue.
Aircraft Engine Makers
GE
GE (General Electric) is a long-established, world-leading general electronics manufacturer with its origins in the Edison Electric Lighting Company founded by Thomas Edison in 1878. The company is also famous for its aggressive business portfolio reshuffling, implementing the number one/number two strategy of withdrawing from all businesses except those with the No. 1 or No. 2 global market share. After Jeff Immelt, who made the Industrial Internet a growth strategy, retired, John Flannery, a freshman, became president in 2017, but the management team continues to change, with Larry Culp being brought in from outside Danaher to become the new CEO in 2018. The company announced that GE will be spun off into three separate companies in 2021: a healthcare division, a power and energy division, and an aviation division.
Raytheon Technologies
Raytheon Technologies was created in 2019 through the merger of defense giant Raytheon and United Technologies Group. The former United Technologies Group spun off its elevator business Otis and its air conditioning business Carrier in 2020, and now owns Pratt & Whitney, an aircraft engine company; Collins Aerospace, a provider of systems for commercial aircraft; and Raytheon, which manufactures space defense equipment, is the core business.
Safran
Safran is a leading defense and telecommunications company based in France. It manufactures aircraft engines for civilian and military applications through its Snecma subsidiary. In 2018, it acquired Zodiac, which is strong in in-flight entertainment, seating, and catering equipment.
Honeywell International
Honeywell is a U.S.-based conglomerate founded in 1886. The company has a wide range of products including aircraft engines, electronic control equipment, automation equipment, specialty materials, and automotive components. In 2017, the company spun off its turbocharger, residential air conditioning, and fire alarm businesses.
Rolls-Royce
Rolls-Royce is an aircraft and marine engine manufacturer based in the United Kingdom. It has the same roots as Rolls-Royce in automobiles. The company was nationalized by the British government for a time, but has grown through aggressive acquisitions, including a subsidiary aircraft engine business with BMW of Germany. Civil Aviation, Defense, and Power Systems are the three pillars of the company. In industrial diesel engines, the company manufactures and sells engines for power plants, construction equipment, railroads, and ships, competing with Caterpillar, Cummins, GE, and others. The commercial marine sector has been weak and has accelerated restructuring since 2018. L'Orange, a fuel injector company, was sold to Woodward, a US aircraft parts manufacturer. In marine engines, the company's main products are high-speed engines under the MTU brand and medium-speed engines under the Bergen brand, but it sold Bergen to JSC Transmashholding, a major Russian railcar manufacturer, in 2021.
CFM International
CFM International, headquartered in Paris, France, manufactures and supports the CFM56 series jet engines. It is a joint venture between GE of the United States and Safran of France (both companies own 50%).
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Kawasaki Heavy Industries is one of Japan's leading manufacturers of space defense and heavy electric machinery, with its origins in the Kawasaki Tsukiji Shipyard, established in 1896 by Shozo Kawasaki with the support of Masayoshi Matsukata. In addition to Kawasaki Shipbuilding (Kawasaki Heavy Industries), Kawasaki Kisen and Kawasaki Steel (JFE) belonged to the prewar Kobe Kawasaki Zaibatsu. The company has an excellent reputation for training engineers. Today, Kawasaki develops and manufactures general-purpose engines for defense, aero engines, rolling stock, plants, hydraulic equipment, industrial robots for welding and silicon ware transport, shipbuilding, medium and large motorcycles, off-road four-wheelers, personal watercraft (marketed under the Jet Ski trademark), and agricultural machinery.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, founded in 1884, is one of Japan's leading heavy industry groups. It is considered one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group. Before WWII, the company grew as a military-industrial complex. During the war, it worked on the battleship Musashi and the Zero fighter, and has maintained the world's highest level of technological capability since that time. After the war, the company strengthened its heavy engineering field for the civilian market, manufacturing and selling power plant systems, aircraft engines, aircraft, ships, turbochargers, forklifts, mechanical systems, engineering, and defense-related equipment.








